City Geoinformation System
The City Geoinformation System is a web resource created for the collection, storing, displaying and analyzing of spatial and related information about the objects, processes and phenomena of the city as a whole.
Municipalities use the city geoinformation system (GIS) to get regulated access to reliable and relevant city data, while vastly reducing the amount of time spent on searching, analyzing and generalizing data.
The city GIS provides support for arriving at optimum management decisions on developing the territory of the municipal entity, based on providing consistent and complete, objective information about available territorial resources, real estate objects, engineering and transport infrastructure, as well as planned and developing changes to any city entity. All such information is gathered and distributed within the guidelines of applicable law.
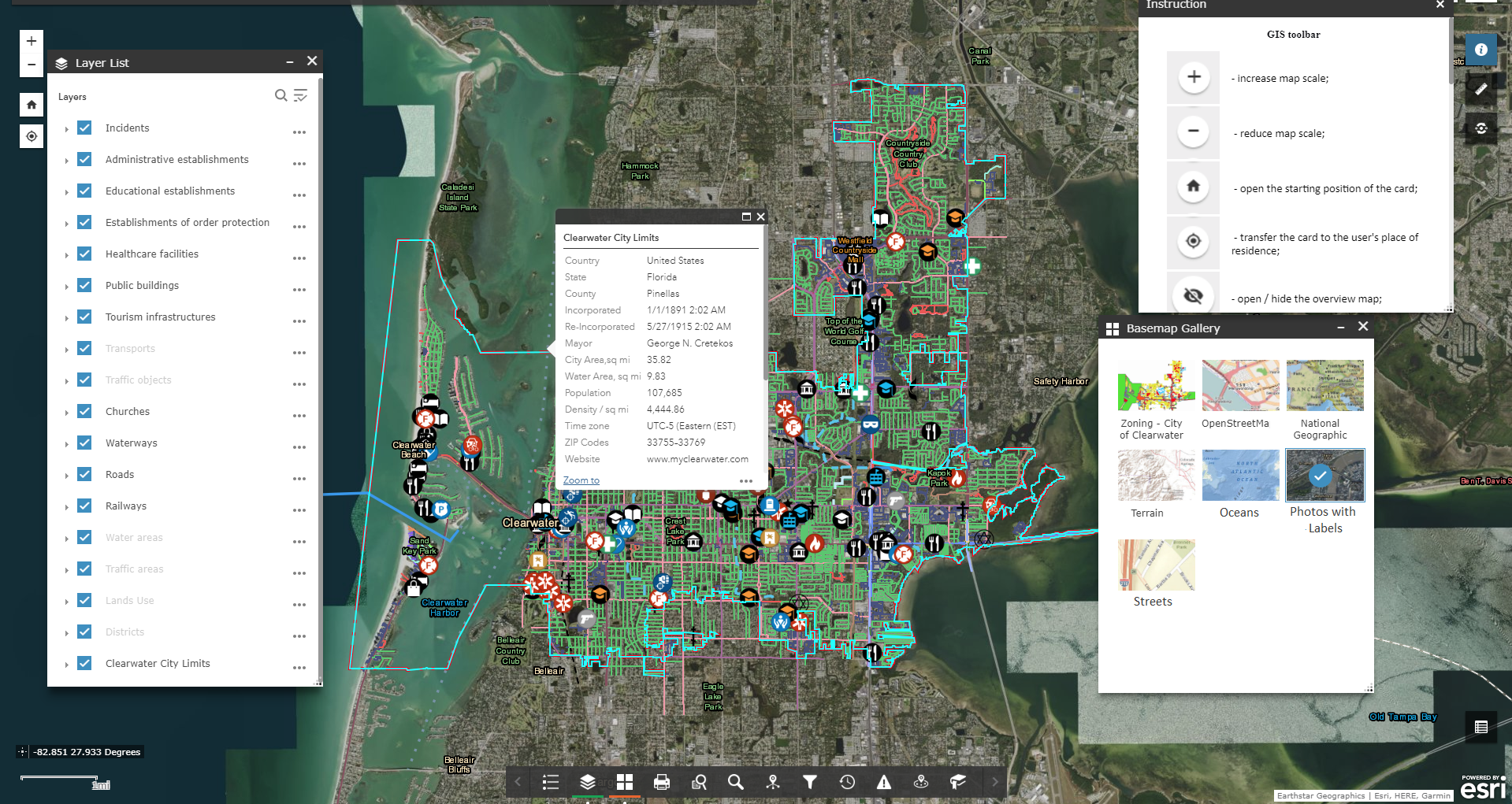
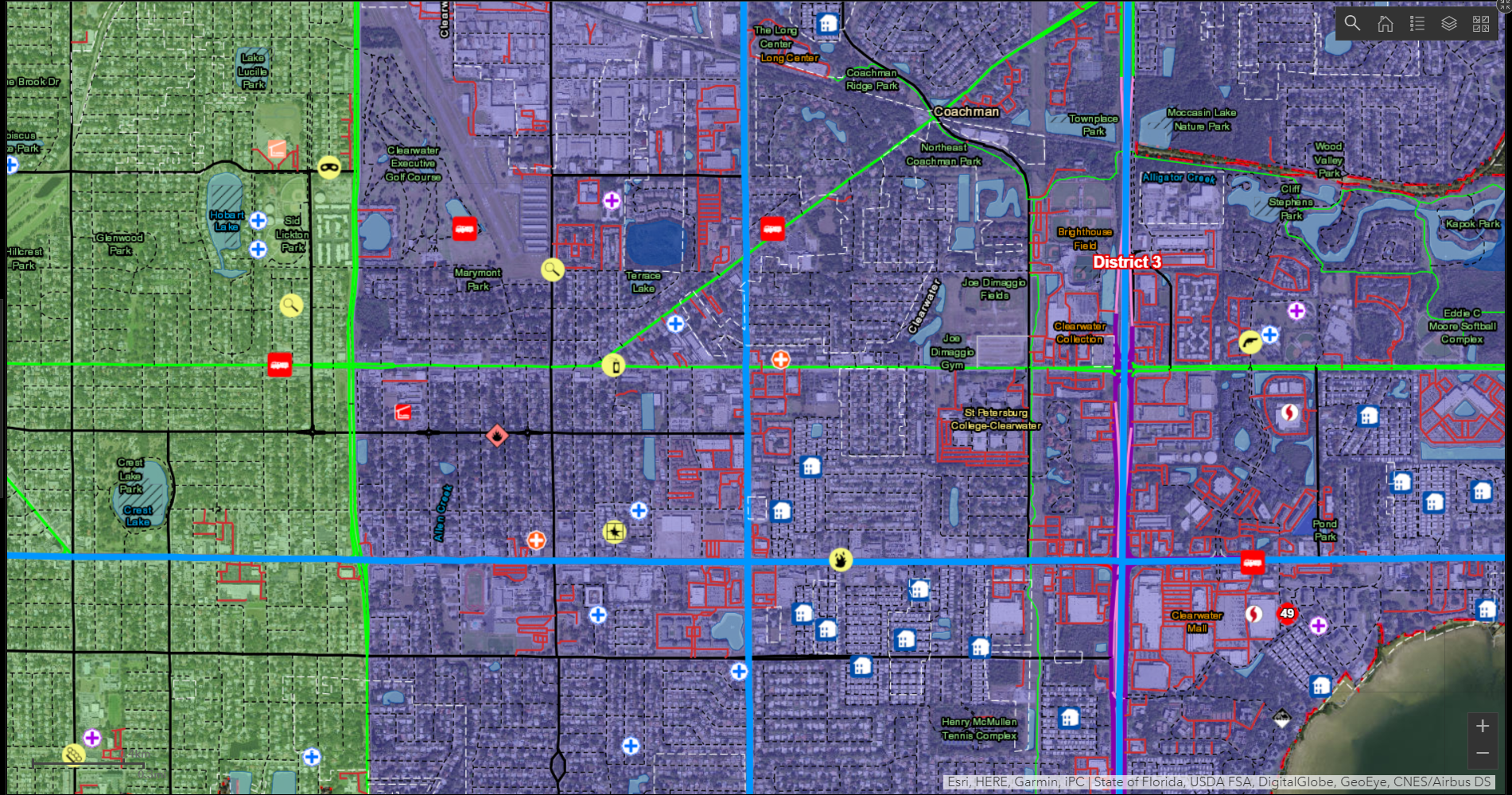

Create a comfortable city environment based on the GIS of the city
GIS technology now makes it possible to:
- form a single information space of the city containing information about the territory, regulations on its use, real property entities, and existing transport and engineering infrastructure;
- computerize management of documents for solving issues in the field of urban planning on the basis of cartographic materials;
- develop a professional municipal information infrastructure;
- automate the processes of preserving and updating information about the objects of the urban environment, thus greatly enhancing its reliability and effectiveness;
- provide local governments, city support organizations and citizens with reliable information about the territory of the city;
- provide information and process support to others in the field of territorial administration and the analysis and forecasting of urban environmental development.
Advantages of implementing an urban Geoinformation system
- a single geographic software program for providing of local government solutions that align with other legislative requirements;
- scalability and flexibility of a software solution aligned with existing constraints and urgencies;
- the small cost of basic modules or components of the system;
- regulation of access to spatial data and other information;
- an efficient tool for full and rapid data exchange among units and departments;
- convenient and popular e-service for local citizens, companies and institutions;
- reduced costs of collecting, processing and maintaining cartographic and other spatial information for immediate use, as a quick return on investment;
- adherence to national and international standards and formats of data exchange;
- the automation of many routine procedures.

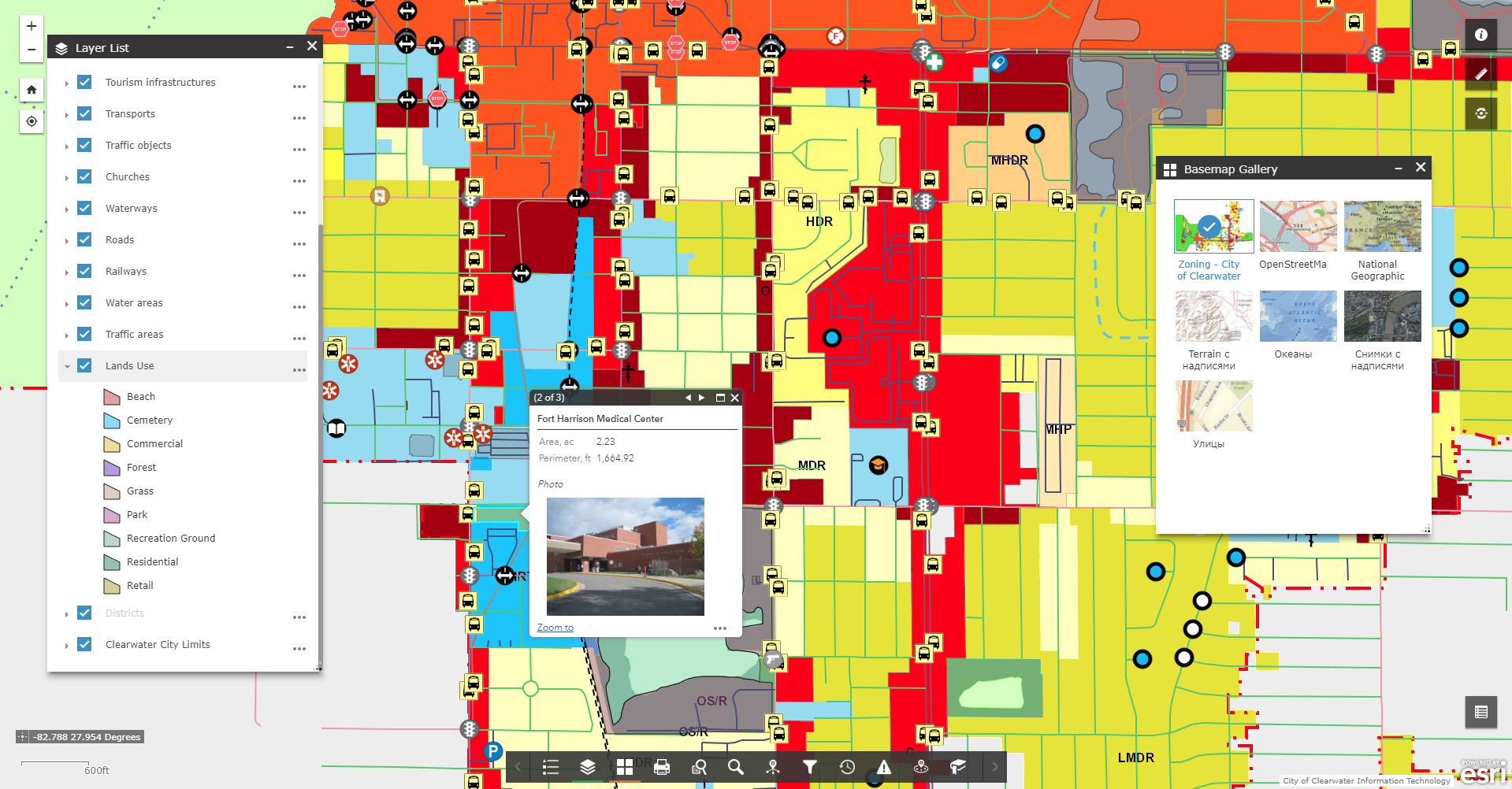

The approximate structure of the city's GIS database
- Basic geographic data resources: a single cartographic basis (a unified orthophoto plan, digital topographic and geodetic data, site plan, zoning plan) with a register of geographical names (streets and rivers), a layer of buildings and structures, etc.;
- Thematic data sources are supplemented with the corresponding attributive component: a network of engineering communications, a register of urban planning conditions and constraints, temporary constructions (Small Architectural Forms), advertising structures, natural resources, architectural monuments, medical institutions, educational and cultural institutions, industrial and financial objects, and others;
- Integrated or problem-oriented information resources: building restriction areas (water protection, environmental and sanitary protection zones, red lines), highway areas with current repair operations, etc.

